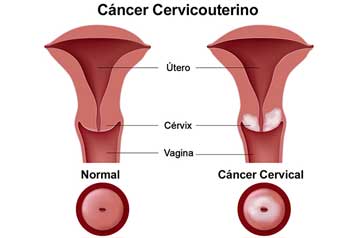
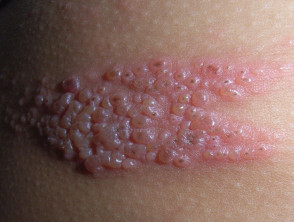
Human Papillomavirus (HPV)
What is Genital Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Infection?
Genital human papillomavirus (also called HPV) is the most common sexually transmitted infection (STI).
There are more than 40 HPV types that can infect the genital areas of males and females.
These HPV types can also infect the mouth and throat.
Most people who become infected with HPV do not even know they have it. HPV is not the same as herpes or HIV (the virus that causes AIDS).
These are all viruses that can be passed on during sex, but they cause different symptoms and health problems.
How do people get HPV?
HPV is passed on through genital contact, most often during vaginal and anal sex.
HPV may also be passed on during oral sex and genital-to-genital contact.
HPV can be passed on between straight and same-sex partners—even when the infected partner has no signs or symptoms.
A person can have HPV even if years have passed since he or she had sexual contact with an infected person.
Most infected persons do not realize they are infected or that they are passing the virus on to a sex partner. It is also possible to get more than one type of HPV.
Very rarely, a pregnant woman with genital HPV can pass HPV to her baby during delivery.
In these cases, the child can develop Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis (RRP), a rare condition in which warts grow in the throat.
In children, this is also referred to as juvenile-onset Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis (JORRP).
Source
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Related Topics
-
-
Human Papillomavirus
-
Human Papillomavirus Vaccines: Questions and Answers
-
Human Papilloma Virus Signs and Symptoms
-
Human Papillomavirus Screening
-
Cervical Cancer Screening Tests
-
What Does My Pap Test Result Mean?
-
What Does My HPV Test Result Mean?
-
HPV Test FDA's Approval
-
Human Papillomavirus Treatment
-
Human Papillomavirus Prevention
-
Human Papillomavirus and Men
-
HPV and Men
-
Human Papillomavirus Infection Treatment
-
Human Papillomavirus and Genital Warts
-
Human Papillomavirus Associated Cancers
United States, 2004–2008 -
Preventing Cervical Cancer Worldwide (PDF document)
-
-
Vaccine
-
Human Papillomavirus Vaccine
-
FDA Advisory Panel Recommends Human Papillomavirus Vaccine
-
Reports of Health Concerns Following HPV Vaccination
-
Human Papillomavirus Fainting (Syncope) After Vaccination
-
Human Papillomavirus Frequently Asked Questions on Syncope After Vaccination