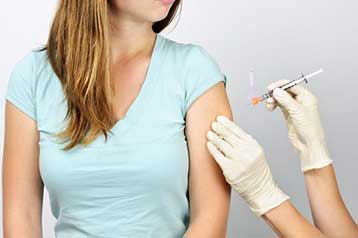
Preconception risk factors for adverse pregnancy outcomes
- Isotretinoins. Use of isotretinoins (e.g., Accutane®) in pregnancy to treat acne can result in miscarriage and birth defects. Effective pregnancy prevention should be implemented to avoid unintended pregnancies among women with childbearing potential who use this medication.
- Alcohol misuse. No time during pregnancy is safe to drink alcohol, and harm can occur early, before a woman has realized that she is or might be pregnant. Fetal alcohol syndrome and other alcohol-related birth defects can be prevented if women cease intake of alcohol before conception.
- Anti-epileptic drugs. Certain anti-epileptic drugs are known teratogens (e.g., valproic acid). Recommendations suggest that before conception, women who are on a regimen of these drugs and who are contemplating pregnancy should be prescribed a lower dosage of these drugs.
- Diabetes (preconception). The three-fold increase in the prevalence of birth defects among infants of women with type 1 and type 2 diabetes is substantially reduced through proper management of diabetes.
- Folic acid deficiency. Daily use of vitamin supplements containing folic acid has been demonstrated to reduce the occurrence of neural tube defects by two thirds.
- Hepatitis B. Vaccination is recommended for men and women who are at risk for acquiring hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection. Preventing HBV infection in women of childbearing age prevents transmission of infection to infants and eliminates risk to the woman of HBV infection and sequelae, including hepatic failure, liver carcinoma, cirrhosis, and death.
- HIV/AIDS. If HIV infection is identified before conception, timely antiretroviral treatment can be administered, and women (or couples) can be given additional information that can help prevent mother-to-child transmission.
- Hypothyroidism. The dosages of Levothyroxine® required for treatment of hypothyroidism increase during early pregnancy. Levothyroxine® dosage needs to be adjusted for proper neurologic development of the fetus.
- Maternal phenylketonurea (PKU). Women diagnosed with PKU as infants have an increased risk for delivering neonates/infants with mental retardation. However, this adverse outcome can be prevented when mothers adhere to a low phenylalanine diet before conception and continue it throughout their pregnancy.
- Rubella seronegativity. Rubella vaccination provides protective seropositivity and prevents congenital rubella syndrome.
- Obesity. Adverse perinatal outcomes associated with maternal obesity include neural tube defects, preterm delivery, diabetes, cesarean section, and hypertensive and thromboembolic disease. Weight loss before pregnancy reduces these risks.Appropriate weight loss and nutritional intake before pregnancy reduces these risks.
- Oral anticoagulant. Warfarin, which is used for the control of blood clotting, has been demonstrated to be a teratogen. To avoid exposure to warfarin during early pregnancy, medications can be changed to a nonteratogenic anticoagulant before the onset of pregnancy.
- Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) . Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae have been strongly associated with ectopic pregnancy, infertility, and chronic pelvic pain. STDs during pregnancy might result in fetal death or substantial physical and developmental disabilities, including mental retardation and blindness. Early screening and treatment prevents these adverse outcomes.
- Smoking. Preterm birth, low birthweight, and other adverse perinatal outcomes associated with maternal smoking in pregnancy can be prevented if women stop smoking before or during early pregnancy. Because only 20% of women successfully control tobacco dependence during pregnancy, cessation of smoking is recommended before pregnancy.
Several providers and maternal and child health researchers have recommended that health risks and behaviors be addressed during any encounter with the health-care system because approximately half of pregnancies in the United States are unintended. One clinical trial has indicated that provision of preconception care can increase pregnancy planning and intention. This finding is vital because studies have consistently demonstrated that planned pregnancies typically have improved outcomes for both women and infants.
Source
Recommendations to Improve Preconception Health and Health Care --- United States (April 21, 2006)
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
GeoSalud, August 11, 2013