Infertility and Fertility
"Infertility" is a term used to describe the inability of a woman or man to conceive a child or the inability of a woman to carry a pregnancy to term. Infertility is defined clinically in women and men who cannot achieve pregnancy after 1 year of having sex without using birth control and in women who have two or more failed pregnancies.
In women older than age 35, the time frame is reduced to 6 months to indicate that earlier evaluation in this age group is appropriate, because fertility declines as a woman gets older.
Many different medical conditions and other factors can contribute to fertility problems, and an individual case may have a single cause, several causes, or—in some cases—no identifiable cause.
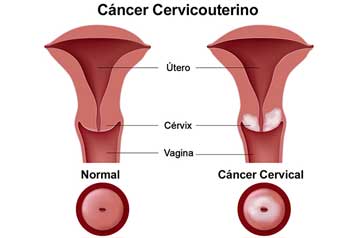
The term "infertility" also is used to describe women who are able to get pregnant but who are unable to carry a fetus to term. If loss of the pregnancy occurs before 20 weeks of pregnancy, it is called a miscarriage or clinical spontaneous abortion. Losses after 20 weeks are called stillbirths. Multiple losses of pregnancy are called repeated or recurrent miscarriage.
How common is infertility for men and women?
Studies suggest that after 1 year of having unprotected sex, 15% of couples are unable to conceive, and after 2 years, 10% of couples still have not had a successful pregnancy.
In couples younger than age 30 who are generally healthy, 20% to 37% are able to conceive in the first 3 months. However, aging of the female partner affects fertility. After age 30, a woman's chances of getting pregnant decrease rapidly every year.